Design Tools for your Toolbox
Attention to design continues to become more prevalent as organizations look for new ways to bring meaningful products to customers. Although these techniques are not new, they are becoming hot topics as teams look for new ways to innovate. In this article we will briefly go through design techniques, how to use them, and when.

Design Thinking
Design Thinking is a great tool to use in the earliest stages of an innovation project. This method begins with finding a pain point customers have. A set of customers are interviewed to understand the root causes of that pain point. Then the team determines if there is a viable business case to move forward.
Here are the 5 steps that are part of Design Thinking:
EMPATHY
Gather Data from the customer, listen to the user and try to “walk in their shoes”. Be mindful of new insights and learnings.
REFRAME
Are we solving the right challenge? For example, do people get parking tickets because they are late or forgetful to top up the meter? After talking to the customers, you may find it’s the payment process being inconvenient and difficult to get back to their .
IDEATE
Brainstorming and generating lots of ideas on potential solutions. Then narrow down the top ideas.
PROTOTYPING
Cheap low fidelity solution, a visual representation so your end user can give you feedback on your idea.
TEST
Tweak your prototype based on feedback

Design Sprint
I first learned about the Design Sprint after watching a talk from Kai Haley on how it’s used at Google. The method helps address critical business questions and ensure that you are building the right thing.
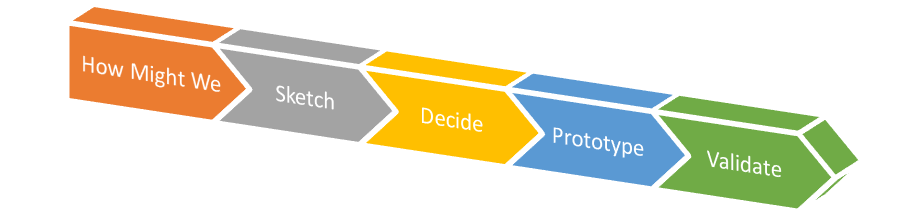
HOW MIGHT WE
Team members prepare ideas (one idea per sticky) considering ‘how might we transform paint points into opportunities’ For example how might we make finding a general contractor easier?
Next, the team share and affinity map ideas – grouping the opportunities of How Might We stickies. Prioritize the opportunities for the biggest impact.
Another way is to chart out in detail the customer journey. Highlighting pain points as you go.
SKETCH
Generate a broad range of ideas for potential solutions in a time box.
Suggested technique: Crazy 8s – Give each participant 8 minutes to generate 8 sketches. Sometimes people get stuck on their first sketch. This technique is meant to push you to get unstuck!
DECIDE
The team decides as a group what to include in the prototype. Suggested technique: Dot Voting or some form of anonymous voting.
PROTOTYPE
Less than a day, the team will create a real enough prototype to test out their Sprint questions. They create static mocks that can be clicked through.
VALIDATE
Taking the final prototype to the live users. This provides the critical feedback for a team to know what they should build. Users are potential customers. Also important is the Stakeholder review, and a Technical Feasibility review.
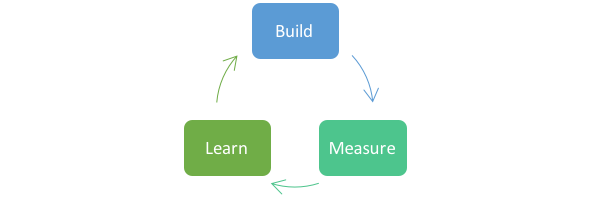
Lean Startup
Creating a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) that’s fit for purpose by building a minimum set of features that satisfy users. The method of Build Measure Learn is repeated as the MVP is refined to improve & adapt its fit for purpose. To learn more about this technique, who best to explain it than the creator Eric Ries.
What's Similar or Different About These Tools?
All of these methods are great tools for your team’s creative toolbox. However how they are used is important to note.
A Design Sprint differs from Design Thinking in the sense that the former is a formal process, and the later is a mindset and philosophy. Design Thinking is a step-by-step system for producing and testing ideas. It’s a systematic way of doing a Design Thinking. Now Design Thinking has no time boxes and puts a greater emphasis on empathizing with the customer’s needs.
Lean Startup is an excellent method to use after your Design Sprint, or Design Thinking outcomes. Build the initial product. Test your product in the market and its impact (Measure), incorporate the initial feedback into the next product iteration (Learn).
When your product strategies get stuck and we don’t know what to do next, these tools are a great way to reinvigorate life into it. Get unstuck, test and learn!

